Summary
The top cybersecurity challenges for SMEs include a lack of security awareness and training, limited budgets and resources, the increasing sophistication of attacks like ransomware and deepfakes, the insecurity of remote work and personal devices, a shortage of cybersecurity talent, and difficulties with compliance.
Other challenges include weak password and credential management, keeping software updated, and underestimating their risk of being targeted by cybercriminals.
OnAir Post: Small and Medium Enterprises Challenges
About
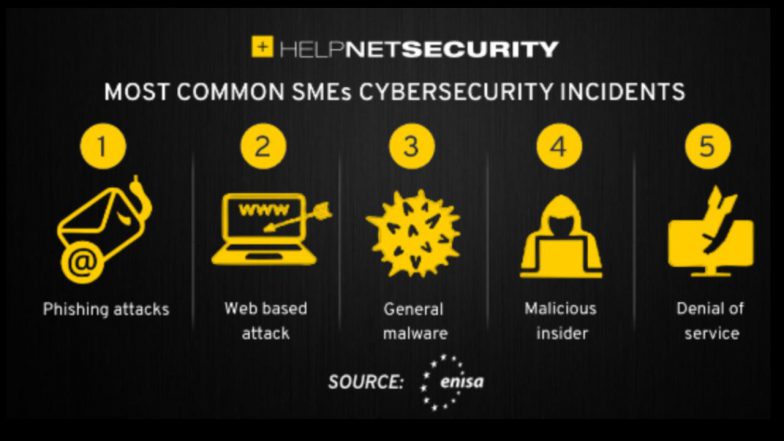
Small and Medium Enterprises Challenges
- Lack of employee training: Many SMEs fail to provide adequate cybersecurity training on threats like phishing and deepfakes, leaving them vulnerable to human error.
- Limited resources and budget: Small businesses often have constrained budgets, making it difficult to invest in robust security solutions and expertise.
- Sophisticated threats: SMEs face increasingly advanced threats, including ransomware that can lock down critical data and deepfake technology used for social engineering.
- Remote and hybrid work: A hybrid or remote workforce introduces new vulnerabilities, especially concerning data access on personal devices and unsecured networks.
- Shortage of cybersecurity professionals: There is a significant lack of in-house cybersecurity talent, forcing SMEs to go without expert guidance or support.
- Weak access control: Inadequate security measures like using weak or reused passwords and a lack of multi-factor authentication (MFA) make it easier for attackers to gain access.
- Unpatched software and outdated systems: Neglecting to update software and operating systems leaves systems vulnerable to known exploits.
- Underestimating risk: Many SMEs incorrectly believe they are too small to be a target or that being attacked once means they won’t be again, leading to a false sense of security.
- Compliance and regulations: Navigating and complying with various data protection regulations can be a significant challenge for SMEs with limited legal and IT staff.
- Poor incident response planning: A lack of a clear, proactive incident response plan means that when an attack does occur, the business is unprepared to contain and recover from it, leading to greater financial and reputational damage.
Web Links
Innovations
- AI-Powered Security: AI is used to analyze threats in real-time, detect anomalies, and automate responses, making it more effective against sophisticated attacks, notes Fortinet.
- Zero Trust Architecture: An evolution from perimeter-based security, this model assumes no user or device can be trusted by default, requiring strict verification for all access requests, explains SentinelOne.
- Cloud Security Solutions: As more businesses move to the cloud, innovations include cloud-native protection, web application firewalls (WAFs), and unified platforms to secure cloud environments, says Microsoft and Fortinet.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): More advanced than traditional antivirus, EDR provides continuous monitoring and response capabilities for endpoints like laptops and mobile devices.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): SIEM platforms aggregate and analyze security data from across an organization to detect and alert on potential threats.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): This is becoming a standard, with improved MFA solutions providing a much stronger layer of security than passwords alone, notes Kaspersky.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): DLP tools help prevent sensitive data from leaving the organization through email, cloud uploads, or other channels.
- Network Segmentation: Dividing a network into smaller, isolated segments limits the “blast radius” of a breach, making it harder for attackers to move laterally across the network, says Cynet.
- Supply Chain Security: Innovations focus on mitigating risks from third-party vendors and software by providing better visibility and control over the software supply chain, notes SentinelOne.
- Automated Security Patching: Tools that automatically apply security patches and updates to software and systems reduce the risk of exploits targeting known vulnerabilities, according to Cyber Defense Magazine.