About
Retail and E-commerce Challenges
- AI-Powered Cyberattacks
Cybercriminals are increasingly using Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning to automate and enhance their attacks, such as generating highly convincing phishing emails (deepfakes, vishing), creating adaptive malware that evades traditional detection, and automatically scanning for vulnerabilities at machine speed. - Advanced Ransomware
Ransomware remains one of the most prevalent and financially damaging threats. Attacks are becoming more sophisticated, often involving double or triple extortion tactics where data is not only encrypted but also stolen and threatened to be leaked. The rise of Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) has lowered the barrier to entry for criminals. - Supply Chain Vulnerabilities
The complex, interconnected ecosystems of IT and telecom rely on a vast network of third-party vendors and suppliers. Exploiting a single weak link in the supply chain can compromise multiple organizations simultaneously, as seen in major incidents involving software updates or third-party hardware. - Cloud Security Risks
As businesses migrate critical workloads and sensitive data to multi-cloud environments, new vulnerabilities arise, primarily from security misconfigurations, insecure APIs, and inadequate identity and access management (IAM) practices. - IoT and 5G Security Risks
The rapid proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices and the rollout of 5G networks significantly expand the attack surface. Many IoT devices are designed with inadequate security, making them easy targets for use in large-scale botnets and DDoS attacks or as entry points into corporate networks. - Phishing and Social Engineering
These human-centric attacks remain highly effective, exploiting human trust and error to steal credentials or deploy malware. The use of AI to create highly personalized and believable scams (spear-phishing, deepfakes) exacerbates this challenge. - Insider Threats
Employees, contractors, or business partners who misuse their legitimate access, either maliciously or through negligence, pose a significant risk. These threats can lead to data theft, operational sabotage, and can be difficult to detect with traditional security measures. - Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) Attacks
DDoS attacks continue to be a major concern, particularly in the telecommunications sector where service availability is paramount. Attackers use compromised devices to overwhelm networks and services, often as a smokescreen for other malicious activities. - Vulnerabilities and Patch Management
Threat actors actively target unpatched software, misconfigured systems, and known weaknesses. The challenge lies in managing and prioritizing patches across diverse and often legacy IT infrastructures, a task made more difficult by the sheer scale of modern networks. - Cybersecurity Skills Gap and Awareness
There is a persistent shortage of skilled cybersecurity professionals, making it difficult for organizations to build robust defenses, monitor threats 24/7, and respond effectively to incidents. Furthermore, a lack of general security awareness among employees means human error continues to be a leading cause of breaches.
Source: Gemini AI Overview – 11/3/2025
Web Links
Innovations
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)-Driven Security
AI and ML are used for advanced threat intelligence, analyzing vast amounts of data in real-time to detect anomalies and predict potential vulnerabilities before they can be exploited. This helps automate responses to low-level threats and counter AI-powered attacks launched by cybercriminals. - Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA)
Operating on the principle of “never trust, always verify,” ZTA requires strict identity verification and access controls for every user, device, and application attempting to access network resources, regardless of their location (inside or outside the network perimeter). - Enhanced Authentication: Biometrics and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
To counter identity-based attacks, retailers are increasingly adopting stronger authentication methods. Biometric encryption (fingerprints, facial recognition) and MFA provide essential extra layers of security beyond traditional passwords, significantly reducing the risk of account takeovers. - Secure Payment Solutions & Tokenization
Innovations in secure payment processing involve tokenization, which replaces sensitive customer data (like credit card numbers) with unique, non-sensitive symbols or “tokens” during transactions. This ensures that actual sensitive information is not stored in its original form, minimizing data breach impact. - Cloud Security and Abstractions
As retailers migrate operations to the cloud, robust cloud security solutions are critical. These involve specific controls, shared responsibility matrices, and data security measures (encryption, data masking) to ensure compliance with regulations like GDPR and PCI DSS. - Supply Chain Threat Detection
Given the heavy reliance on third-party vendors and partners, innovations focus on monitoring and assessing third-party risks. This involves implementing regular risk assessments and enhancing monitoring of supply chain activities to mitigate the risk of attacks via external partners. - Web Application Firewalls (WAF) and API Protection
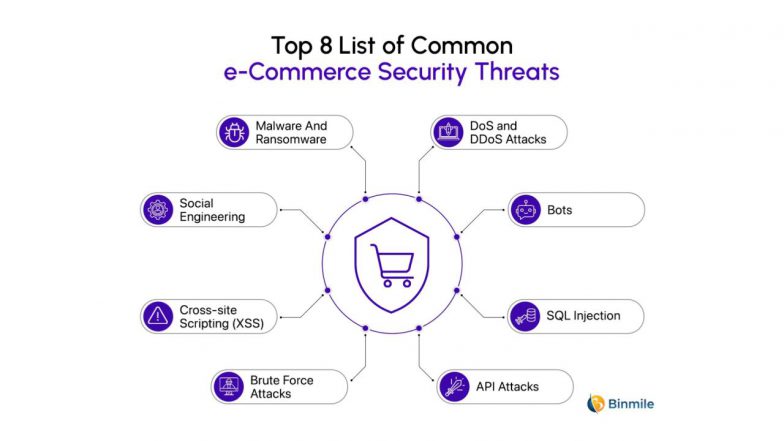
WAFs are crucial for filtering malicious traffic and protecting e-commerce websites and APIs from common attacks like SQL injection and cross-site scripting (XSS). Innovations include cloud-based WAFs with real-time threat intelligence and automated API discovery. - Client-Side Protection & Bot Management
This innovation focuses on securing the customer’s end of the interaction, defending against threats like digital skimming (Magecart attacks), formjacking, and malicious bots that attempt account takeovers or data scraping. - Real-Time Monitoring & Threat Detection (SIEM)
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems collect, analyze, and correlate security logs from various systems across the organization to identify potential security threats and incidents in real-time, allowing for swift incident response. - Blockchain Technology for Transparency and Security
Blockchain offers a potential future innovation for enhancing security in supply chain management and secure transactions by creating an immutable, transparent ledger, which can reduce the risk of data manipulation and fraud.