Summary
This is a list of cybersecurity information technologies. Cybersecurity concerns all technologies that store, manipulate, or move computer data, such as computers, data networks, and all devices connected to or included in said networks, such as routers and switches. All information technology devices and facilities need to be secured against intrusion, unauthorized use, and vandalism. Users of information technology are to be protected from theft of assets, extortion, identity theft, loss of privacy, damage to equipment, business process compromise, and general disruption. The public should be protected against acts of cyberterrorism, such as compromise or denial of service.
Cybersecurity is a major endeavor in the IT industry. There are a number of professional certifications given for cybersecurity training and expertise.[1] Billions of dollars are spent annually on cybersecurity, but no computer or network is immune from attacks or can be considered completely secure.
This article attempts to list important Wikipedia articles about cybersecurity.
Source: Wikipedia
OnAir Post: Cyber Tools
About
Web Links
Videos
Top 8 Cybersecurity Tools 2024 | 8 Tools For Cybersecurity In 2024 | Simplilearn
(18:37)
By: Simplilearn
In this Top 8 Cybersecurity Tools 2024 video, we delve into the future of cybersecurity by presenting the top 8 must-have cybersecurity tools for 2024. Stay ahead of evolving cyber threats with these cutting-edge solutions designed to protect your digital assets and data. From advanced threat detection to robust encryption, we’ll explore the features and benefits of each tool, ensuring you’re well-prepared for the cybersecurity landscape of tomorrow. Don’t miss out on securing your digital world—watch now and equip yourself with the best cybersecurity tools for a safer online experience.
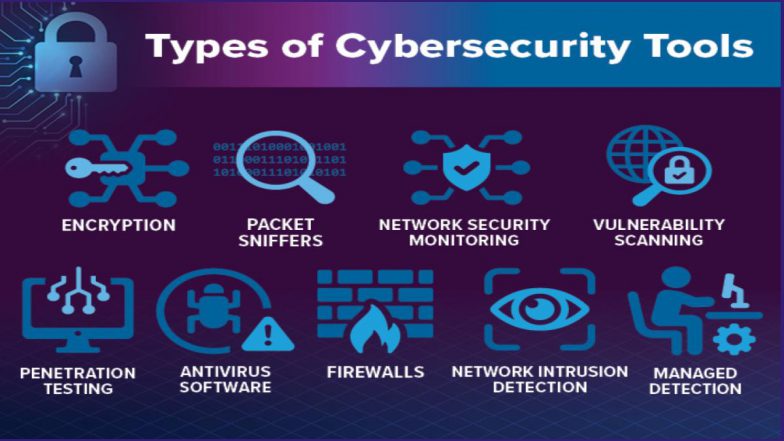
Types of Tools
Source: Other
1. Network security monitoring
- Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS): Actively monitor network traffic and either alert administrators (IDS) or automatically take action (IPS) when a potential threat is detected.
- Packet Sniffers: Capture and analyze data packets in real-time to help identify suspicious traffic patterns and vulnerabilities.
2. Endpoint security
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): Provides continuous monitoring and data collection from endpoints, with the ability to detect, investigate, and respond to threats.
- Antivirus/Anti-Malware: Scans for and removes malicious software, including viruses, worms, spyware, and ransomware.
3. Vulnerability management
- Vulnerability Scanners: Tools like Nessus automate the process of finding security flaws, outdated patches, and misconfigurations.
- Penetration Testing Tools: Simulate attacks on a system to find and evaluate the effectiveness of existing security measures.
4. Identity and access management (IAM)
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Requires multiple forms of verification to prove a user’s identity before granting access.
- Privileged Access Management (PAM): Controls and monitors access to an organization’s most sensitive systems and data.
5. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
6. Cloud security
- Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASBs): Enforce security policies and controls across various cloud services.
- Cloud Workload Protection Platforms (CWPPs): Secure workloads running in public, private, and hybrid cloud environments.
7. Data loss prevention (DLP)
8. Email security
- Email Gateway Security: Inspects incoming emails to filter out malicious content before it reaches a user’s inbox.
9. Web application security
- Web Application Firewalls (WAFs): Filter and monitor web traffic to and from a web application to prevent malicious attacks.
- Web Vulnerability Scanners: Automatically crawl websites to find vulnerabilities.
10. Encryption
Wikipedia
Contents
This is a list of cybersecurity information technologies. Cybersecurity concerns all technologies that store, manipulate, or move computer data, such as computers, data networks, and all devices connected to or included in said networks, such as routers and switches. All information technology devices and facilities need to be secured against intrusion, unauthorized use, and vandalism. Users of information technology are to be protected from theft of assets, extortion, identity theft, loss of privacy, damage to equipment, business process compromise, and general disruption. The public should be protected against acts of cyberterrorism, such as compromise or denial of service.
Cybersecurity is a major endeavor in the IT industry. There are a number of professional certifications given for cybersecurity training and expertise.[1] Billions of dollars are spent annually on cybersecurity, but no computer or network is immune from attacks or can be considered completely secure.
This article attempts to list important Wikipedia articles about cybersecurity.
General
Introductory articles about cybersecurity subjects:
Cryptography
The art of secret writing or code. A "plaintext" message is converted by the sender to "ciphertext" by means of a mathematical algorithm that uses a secret key. The receiver of the message then reverses the process and converts the ciphertext back to the original plaintext.[6]
Cryptography subject matter
- Plaintext
- Ciphertext
- Encryption
- Decryption
- History of cryptography
- Alan Turing
- Cipher
- Cryptanalysis
- Cryptographic primitive
- Cryptographic Service Provider
- HMAC
- HMAC-based One-time Password algorithm
- Cryptographic hash function
- Hash collision
- Hash-based cryptography
- Cryptographic nonce
- Salt (cryptography)
- Cryptographic strength
- Block cipher
- Block cipher mode of operation
- Stream cipher
- Key (cryptography)
- Key size
- Cryptographic key types
- Symmetric-key cryptography
- Public-key cryptography (sometimes called Asymmetric-key cryptography)
- Public-Key Cryptography (conference)
- Digital signature
- Non-repudiation
- Public key certificate
- Certificate authority
- Public key fingerprint
- Secret sharing
- Internet key exchange
- Strong cryptography
- Brute-force attack
- Dictionary attack
- Padding oracle attack
- Pass the hash
Cipher technologies
- Enigma machine
- Caesar Cipher
- Vigenére cipher
- Substitution cipher
- One-time pad
- Beale ciphers
- The Codebreakers[7]
- Data Encryption Standard
- Advanced Encryption Standard
- International Data Encryption Algorithm
- List of hash functions
- Comparison of cryptographic hash functions
- SHA-1
- SHA-2
- SHA-3
- SHA-3 competition
- RSA (cryptosystem)
- X.509
- Pretty Good Privacy
- Diffie-Hellman key exchange
- Blowfish (cipher)
Steganography
Steganography is the process of hiding data within other data, most commonly by hiding data inside images.[8]
Authentication and access
The process by which a potential client is granted authorized use of an IT facility by proving its identity.[10]
- Authentication
- Login
- Password
- Passphrase
- Password strength
- One-time password
- Multi-factor authentication
- Identity management
- Identity management theory
- Identity management system
- Encrypting PIN Pad
- Shared secret
- Authorization
- Access control
- Principle of least privilege
- Cryptographic protocol
- Authentication protocol
- Public key infrastructure
- RADIUS
- Kerberos (protocol)
- OpenID
- OAuth
- Active Directory Federation Services
- Security Assertion Markup Language
- SAML-based products and services
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)
A framework for managing digital certificates and encryption keys.
Tools
Computerized utilities designed to study and analyze the security of IT facilities and/or break into them on an unauthorized and potentially criminal basis.[11]
Threats
Modes of potential attacks on IT facilities.[12]
- Cyberattack
- STRIDE (security)
- Vulnerability (computing)
- Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures
- Privilege escalation
- Social engineering (security)
- Malware
- Spyware
- Backdoor (computing)
- Computer virus
- Computer worm
- Macro virus
- Keystroke logging
- Trojan horse
- Hardware Trojan
- Eavesdropping
- Zombie
- Botnets
- Advanced persistent threat
- Man-in-the-middle attack
- Man-on-the-side attack
- Meet-in-the-middle attack
- Length extension attack
- Replay attack
- Pre-play attack
- Dictionary attack
- Biclique attack
- Denial-of-service attack
- Resource exhaustion attack
- Brute-force attack
- Watermarking attack
- Mangled packet
- Reverse connection
- Polymorphic code
- Password cracking
- Spoofing attack
- POODLE
Exploits
Security exploits affecting computers.[13]
- Exploit (computer security)
- Timeline of computer viruses and worms
- Malware analysis
- XML denial-of-service attack
- Distributed denial-of-service attacks on root nameservers
- Linux malware
- Zero-day (computing)
- Virus hoax
- Pegasus
- Rogue security software
- MS Antivirus (malware)
- Spysheriff
- SpywareBot
- TheSpyBot
- Security Essentials 2010
- Email spam
- Phishing
- Tiny Banker Trojan
- Melissa (computer virus)
- Brain (computer virus)
- CIH (computer virus)
- ILOVEYOU
- Anna Kournikova (computer virus)
- Michelangelo (computer virus)
- Simile (computer virus)
- Stoned (computer virus)
- Acme (computer virus)
- AIDS (computer virus)
- Cascade (computer virus)
- Flame (computer virus)
- Abraxas (computer virus)
- 1260 (computer virus)
- SCA (computer virus)
- ReDoS
- SYN flood
- Billion laughs attack
- UDP flood attack
- Wi-Fi deauthentication attack
- Smurf attack
- Mydoom
- IP address spoofing
- Fork bomb
- WinNuke
Criminal activity
Violation of the law by means of breaking into and/or misusing IT facilities. Laws that attempt to prevent these crimes.[14]
- Computer misuse act
- Cyber-security regulation
- China Internet Security Law
- Computer Crime and Intellectual Property Section
- Cyber criminals
- Cybercrime
- Security hacker
- White hat (computer security)
- Black hat (computer security)
- Industrial espionage § Use of computers and the Internet
- Phreaking
- RDP shop
- Market for zero-day exploits
- 2600 magazine
- Phrack, Google search on “hacker magazine”
- Identity theft
- Identity fraud
- Cyberstalking
- Cyberbullying
Nation states
Countries and their governments that use, misuse, and/or violate IT facilities to achieve national goals.[15]
- Cyber-arms industry
- Computer and network surveillance
- List of government surveillance projects
- Clipper chip
- Targeted surveillance
- United States Cyber Command
- Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency
- National Cybersecurity and Communications Integration Center
- Bletchley Park
- NSO Group
- Hacking Team
- Unit 8200
- NSA
- Room 641A
- Narus (company)
- Equation group
- Tailored Access Operations
- XKeyscore
- PRISM (surveillance program)
- Stuxnet
- Carnivore (software)
End-point protection
The securing of networked computers, mobile devices and terminals.[16]
- Antivirus software
- Comparison of antivirus software
- Lookout (IT security)
- Windows Defender
- Kaspersky Lab
- Malwarebytes
- Avast Antivirus
- Norton AntiVirus
- AVG AntiVirus
- McAfee
- McAfee VirusScan
- Symantec Endpoint Protection
- Microsoft Safety Scanner
- Windows Malicious Software Removal Tool
- VirusTotal
- Application firewall
- Personal firewall
- SentinelOne
Network protection
The protection of the means by which data is moved from one IT facility to another.[17]
- Virtual private network
- IPsec
- Internet Key Exchange
- Internet Security Association and Key Management Protocol
- Kerberized Internet Negotiation of Keys
- Firewall (computing)
- Stateful firewall
- HTTPS
- HTTP Public Key Pinning
- Transport Layer Security
- TLS acceleration
- Network Security Services
- Off the record messaging
- Secure Shell
- Circuit-level gateway
- Intrusion detection system
- Intrusion Detection Message Exchange Format
- Security information management
- Security information and event management
- Security event manager
- Router (computing)#Security
- Security log
- Intranet § Enterprise private network
- Proxy server
Processing protection
The securing of IT facilities that manipulate data, such as computer servers, often by means of specialized cybersecurity hardware.[18]
Storage protection
The protection of data in its non-moving state, usually on magnetic or optical media or in computer memory.[19]
- Disk encryption
- Disk encryption theory
- Disk encryption software
- Comparison of disk encryption software
- BitLocker
- Encrypting File System
- Filesystem-level encryption
- Disk encryption hardware
- Hardware-based full disk encryption
- Personal data
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Privacy policy
- Information security audit
- Information technology audit
- Information technology security audit
Management of security
The processes by which security technology is monitored for faults, deployed and configured, measured for its usage, queried for performance metrics and log files, and/or monitored for intrusions.[20]
Standards, frameworks, & requirements
Officially agreed architectures and conceptual structures for designing, building, and conducting cybersecurity.[21][22]
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework[23][24]
- National Initiative for Cybersecurity Education[25][26]
- Center for Internet Security
- The CIS Critical Security Controls for Effective Cyber Defense[27]
- Cyber Risk Quantification
- Risk management framework[28]
- IT risk[29]
- Risk IT[30]
- ISO/IEC 27000-series
- Cyber-security regulation[31]
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act § Security Rule
- Federal Information Security Management Act of 2002[32]
See also
References
- ^ "CompTIA Career Roadmap". CompTIA. Retrieved 20 Aug 2019.
- ^ Stallings & Brown (2017). Computer Security: Principles and Practice (4 ed.). Pearson. ISBN 978-0134794105.
- ^ Stallings, William (1995). Network and Internetwork Security: Principles and Practice. IEEE Press. ISBN 0-7803-1107-8.
- ^ The Open University (2016). Network security. Kindle.
- ^ Merkow & Breithaupt (2014). Information Security: Principles and Practice (2 ed.). Pearson. ISBN 978-0789753250.
- ^ Stallings, William (2016). Cryptography and Network Security (7th ed.). Pearson. ISBN 978-0134444284.
- ^ Kahn, David (1967). The Code Breakers: The Comprehensive History of Secret Communication from Ancient Times to the Internet. Scribner. ISBN 0-684-83130-9.
- ^ Fridrich, Jessica (2009). Steganography in Digital Media. Cambridge. ISBN 978-0521190190.
- ^ Macrakis, Kristie (2014). Prisoners, Lovers, and Spies: The Story of Invisible Ink from Herodotus to Al-Qaeda. Yale University Press. ISBN 978-0300179255.
- ^ Kao, I Lung (2019). Effective and Efficient Authentication and Authorization in Distributed Systems. University of Florida. ISBN 978-0530003245.
- ^ ICT School (2019). Hacking Tools for Computers. ICT School. ISBN 9781088521588.
- ^ Diogenes & Ozkaya (2018). Cybersecurity--Attack and Defense Strategies. Packt Publishing. ISBN 978-1-78847-529-7.
- ^ Andes, Thomas (8 April 2016). The Encyclopedia of Computer Security Exploits. ISBN 9781530944682.
- ^ Britz, Marjie (2013). Computer Forensics and Cyber Crime (3 ed.). Pearson. ISBN 978-0132677714.
- ^ Kaplan, Fred (2016). Dark Territory: The Secret History of Cyber War. Simon & Schuster. ISBN 978-1476763262.
- ^ Lopez & Setola (2012). Critical Infrastructure Protection. Springer-Verlog. ISBN 978-3642289194.
- ^ Stewart, Michael (2013). Network Security, Firewalls, and VPNs (2 ed.). James & Bartlett Learning. ISBN 978-1284031676.
- ^ Grasser, Michael (2008). Secure CPU: A Secure Processor Architecture for Embedded Systems. VDM Verlag. ISBN 978-3639027839.
- ^ Jacobs & Rudis (2014). Data-Driven Security. Wiley. ISBN 978-1118793725.
- ^ Campbell, T. (2016). Practical Information Security Management: A Complete Guide to Planning and Implementation. APress. ISBN 9781484216859.
- ^ Calder, Alan (28 September 2018). NIST Cybersecurity Framework: A Pocket Guide. IT Governance Publishing Ltd. ISBN 978-1787780422.
- ^ Alsmatti, Izzat (2019). The NICE Cybersecurity Framework. Springer. ISBN 978-3030023591.
- ^ NIST. "Framework for Improving Critical Infrastructure Cybersecurity v1.1" (PDF). NIST. Retrieved 19 Aug 2019.
- ^ NIST (12 November 2013). "Cybersecurity Framework Page". NIST. Retrieved 19 Aug 2019.
- ^ NIST. "NIST SP 800-181: NICE Cybersecurrity Workforce Framework" (PDF). NIST. Retrieved 19 Aug 2019.
- ^ U.S. Congress. "Cybersecurity Enhancement Act of 2014". U.S. Congress. Retrieved 19 Aug 2019.
- ^ Center for Internet Security. CIS Controls V7.1.
- ^ NIST. Special Publication 800-53: Security and Privacy Controls for Federal Information Systems and Organizations (PDF).
- ^ Talabis & Martin (2013). Information Security Risk Assessment Toolkit. Syngress. ISBN 978-1597497350.
- ^ ISACA. The Risk IT Practitioner Guide.
- ^ Kosseff, Jeff (2017). Cyber Security Law. Wiley. ISBN 978-1119231509.
- ^ Taylor, Laura (2013). FISMA Compliance Handbook (2 ed.). Elsevier. ISBN 978-0124058712.